Events Tracking
Fiorano Platform raises an event for any meaningful event that occurs in the system. These System events are collected and processed in the Enterprise Server, and thereby, the state of the artifacts (Event processes, components, server status, and so on) is determined by the sequence of such Events. If the component is configured to raise the monitoring events on the various performance metrics, then these events are also stored in the event repository. The default database is configured as H2 and the database is File-based.
Configuring Event Tracking
The Enterprise Server, by default, is configured to insert all System events into the default H2 Events database (specific database events can be configured for Event Tracking, see next section). If, at any point, the user decides to switch off event tracking, they can do so by opening the profile and navigating to Fiorano > Esb > Events > FESEventsManager (as shown in figure 1) and disabling the EnableSystemEventTracking property (clear the check box).
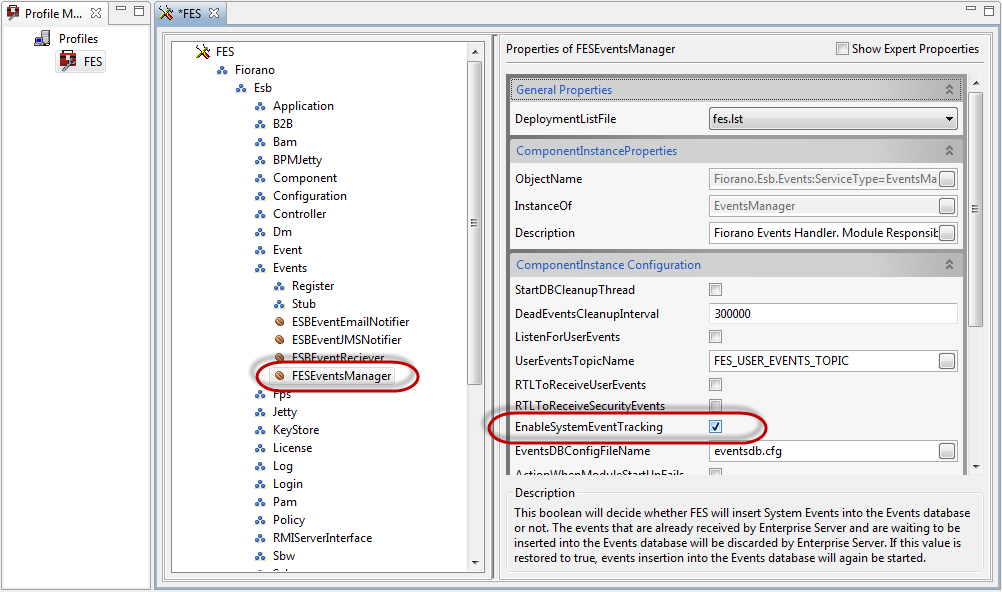
Figure 1: EnableSystemEventTracking property
Server must be stopped to make changes; it can be changed at runtime by logging into FES-JMX.
Another property named 'ListenForUserEvents' (refer to the Enabling ListenForUserEvents parameter for Monitoring Performance section in the Common Configurations page) in the same property panel decides whether or not the Enterprise Server listens to the monitoring events published by component instances. This property, by default, is disabled. If monitoring is enabled for component instances (see Creating Mappings section), this property needs to be enabled so that these user events are recorded.
This property cannot be changed at runtime. Changing this property via FES-JMX connection would require a server restart for the change to take effect. If this property is enabled, EnableSystemEventTracking property decides whether these events will be inserted into the Events database or not.
Disabling Event Tracking
To disable Event Tracking globally, perform the following steps:
- Login to FES-JMX and navigate to Fiorano > Esb > Events > EventsManager > FESEventsManager > config.
- Disable EnableSystemEventTracking property.
Configuring Specific Database
The Event Tracking feature is configured as part of FES to track System and User events into the H2 database running within the Enterprise Server. This can be changed by customizing the eventsdb.cfg file present in: FIORANO_INSTALL_DIR\esb\server\profiles\<profilename>\FES\conf. This file contains all the DB-specific configurations used for event tracking. The default configuration shipped with the installer uses the H2 database; while using a different database, associated values need to be changed.
Do not change the configuration file directly; follow the instructions in the section below.
To view or configure the database, perform the following actions on the Profile Management perspective:
Load the profile and navigate to FES > Fiorano > Esb > Events > FESEventsManager. The Properties of FESEventsManager dialog box on the right displays all the database properties along with their default values.
Property values are editable only for inactive profile nodes. To edit an active profile (a running server), stop the server so that the values become editable.
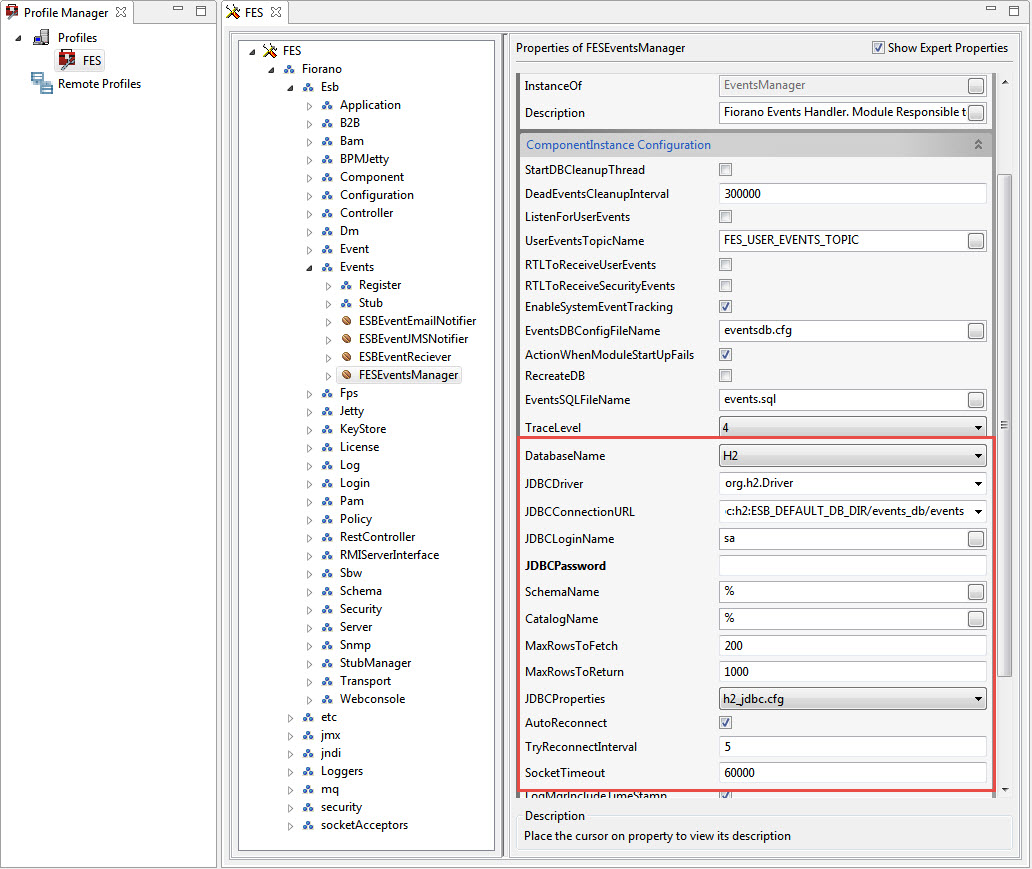
Refer to the Database Property descriptions for descriptions of the SBW database properties.
Select the required database from the Database Name property drop-down and modify values of other properties too accordingly.
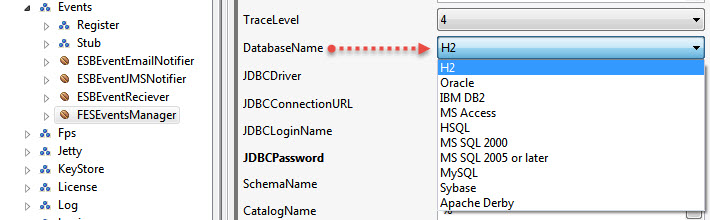
- Click the Save button or press CTRL+S to save the profile changes.
- After configuring a profile to use a database other than the default database, JDBC driver for that database needs to be added under <java.classpath> tag in server startup configuration file (either $FIORANO_HOME/esb/server/bin/server.conf or $FIORANO_HOME/esb/fes/bin/fes.conf, whichever is applicable) prior to starting the Enterprise Server.
- You would have to use the same settings to connect to the DB when using a third-party tool. All database queries used for retrieving workflow-related data is kept in events.sql file.
- When using MS SQL for events tracking, mssql_jdbc.cfg file may need to be configured according to the database driver being used. MSSql 2000 driver follows SQL 99 conventions which quote the SQLState string for table not found exception as '42S02'. On the other hand, MSSQL 2005 driver follows XOPEN SQLState conventions which quote the same SQLState string as 'S0002'. By default, all FES profiles are configured according to the standards followed by the MSSql 2000 driver. If someone uses MSSql 2005 database, or uses the MSSql 2005 driver for MSSql 2000 (2005 driver is backward compatible with 2000 driver and can be used), then the file has to be re-configured accordingly.
It is strongly recommended that the User employ a commercial-grade DB in a production system.
For File-based databases like apache and HSQL, the default location is in the ESB_USER_DIR (which is set in fiorano_vars script). The user has to give the complete path with these variables resolved when using the JDBC URL in a third-party tool.
Example
The default H2 DB JDBC URL is configured as ESB_DEFAULT_DB_DIR/events_db;create=true which resolves to ESB_USER_DIR/EnterpriseServers/<profilename>/FES/events_db and further into something like C:\Program Files\Fiorano\<Fiorano 10ProductVersion>\runtimedata\EnterpriseServers\<profileName>\FES\events_db depending on the actual settings.
Database Property descriptions
| Database Name | JDBC Driver | JDBC Connection URL (Default Formats) | JDBC Properties |
| H2 | org.h2.Driver | jdbc:h2:ESB_DEFAULT_DB_DIR/events_db/events;DB_CLOSE_ON_EXIT=FALSE | h2_jdbc.cfg |
| Oracle | oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver | jdbc:oracle:thin:<ip-address>:<port>:<databaseName> | oracle8_jdbc.cfg |
| IBM DB2 | sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver | jdbc:odbc:sample | db2_jdbc.cfg |
| MS Access | sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver | jdbc:odbc:Driver={Driver do Microsoft Access (*.mdb)};DBQ=D:\\tif\\bin\\sp\\events.mdb` | msaccess_jdb.cfg |
| HSQL | org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver | jdbc:hsqldb:ESB_DEFAULT_DB_DIR/events_db/events | hsql_jdbc.cfg |
| MS SQL 2000 | com.microsoft.jdbc.sqlserver.SQLServerDriver | jdbc:microsoft:sqlserver://<ip-address>:<port>;SelectMethod=Cursor | mssql_jdbc.cfg |
MS SQL 2005 or later | com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver | jdbc:sqlserver://<ip-address>:<port>;databaseName=<databaseName>;SelectMethod=Cursor | mssql_jdbc.cfg |
| MySQL |
|
| mysql_jdbc.cfg |
| Sybase | com.sybase.jdbc2.jdbc.SybDriver | jdbc:sybase:Tds:<ip-address>:<port>/<databaseName> | sybase_jdbc.cfg |
| Apache Derby | org.apache.derby.jdbc.EmbeddedDriver | jdbc:derby:ESB_DEFAULT_DB_DIR/events_db;create=true
| derby_jdbc.cfg |
| Postgre SQL | org.postgresql.Driver | jdbc:postgresql://<ip-address>:<port>/<databasename> | pgsql_jdbc.cfg |
Descriptions of common properties are listed below:
| Properties | Descriptions | Default Value |
| JDBC Login Name | Username to be used for jdbc database connection | <DB dependent> |
| JDBC Password | Password to be used for jdbc database connection | <DB dependent> |
| Scheme Name | By default, the schema name will be %, i.e., all schemas are searched. Schema name is case sensitive | % |
| Catalog Name | By default, the catalog name will be %, all catalogs. Catalog Name for MS SQL should be configured as database name. | % |
| Max Rows To Fetch | Maximum No Of Rows to Fetch. | 200 |
| Max Rows To Return | Maximum No Of Rows to Return. | 1000 |
| Auto Reconnect | Boolean to specify whether SP should try for reconnection with DB automatically. | Enable/Disable |
| Try Reconnect Interval | Interval (in secs) after which SP tries to reconnect with DB in case of a break in connection. | 5 |
| Insert Thread Count | Number of threads used for inserting SBW data into the database. | 1 |
| Support Master Table | Enable if backward compatibility with earlier SBW schema (1001) is required. | Enable/Disable |
| Representable Data Types | Enable to store MESSAGE in representable data format. | Enable/Disable |
| Socket Timeout | Read timeout while reading from the socket. |
|
| Num User IDs | Number of user-defined document IDs the user wants to use in the setup. Num User IDs can be set only once at the creation of the database; to change this value, take a backup of the current database and use a new one. | 1 |
Database Table Structure
The exact schema of the tables varies from database to database according to the configurations provided in <dbtype>_jdbc.cfg file. An explanation of the tables and the various fields is given below:
Table name: TPS_EVENTS & TES_EVENTS
| Column Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
EVENT_ID | INTEGER | Auto Generated |
EVENT_CATEGORY | VARCHAR(255) | Category of event i.e. Information, Warning or Error |
GENERATION_DATE | TIMESTAMP | Time at which the event was generated |
EVENT_SOURCE | VARCHAR(255) | Server name which generated the event |
EVENT_SCOPE | VARCHAR(255) | Scope of the event |
EVENT_MODULE | VARCHAR(255) | Module to which the event belongs |
DESCRIPTION | VARCHAR(255) | Short description of the event |
EVENT_STATUS | VARCHAR(255) | Event constant representing the type of event |
EXPIRY_TIME | TIMESTAMP | Event expiry time |
Table name: SERVICE_EVENTS
| Column Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
EVENT_ID | INTEGER | Auto Generated |
EVENT_CATEGORY | VARCHAR(255) | Category of event i.e. Information, Warning or Error |
GENERATION_DATE | TIMESTAMP | Time at which the event was generated |
EVENT_SOURCE | VARCHAR(255) | Server name which generated the event |
EVENT_SCOPE | VARCHAR(255) | Scope of the event |
EVENT_MODULE | VARCHAR(255) | Module to which the event belongs |
DESCRIPTION | VARCHAR(255) | Short description of the event |
EVENT_STATUS | VARCHAR(255) | Event constant representing the type of event |
EXPIRY_TIME | TIMESTAMP | Event expiry time |
SERVICE_GUID | VARCHAR(255) | The GUID of the service to which the event belongs |
SERVICE_VERSION | VARCHAR(255) | The service version to which the event belongs |
SERVICE_INST_NAME | VARCHAR(255) | Service Instance name |
APP_GUID | VARCHAR(255) | Application Name |
Table name: APPLICATION_EVENTS
| Column Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
EVENT_ID | INTEGER | Auto Generated |
EVENT_CATEGORY | VARCHAR(255) | Category of event i.e. Information, Warning or Error |
GENERATION_DATE | TIMESTAMP | Time at which the event was generated |
EVENT_SOURCE | VARCHAR(255) | Server name which generated the event |
EVENT_SCOPE | VARCHAR(255) | Scope of the event |
EVENT_MODULE | VARCHAR(255) | Module to which the event belongs |
DESCRIPTION | VARCHAR(255) | Short description of the event |
EVENT_STATUS | VARCHAR(255) | Event constant representing the type of event |
EXPIRY_TIME | TIMESTAMP | Event expiry time |
APP_GUID | VARCHAR(255) | The Event Process GUID |
APP_NAME | VARCHAR(255) | The Event Process Name |
Table name: SECURITY_EVENTS
| Column Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
EVENT_ID | INTEGER | Auto Generated |
EVENT_CATEGORY | VARCHAR(255) | Category of Event, that is, Information, Warning or Error |
GENERATION_DATE | TIMESTAMP | Time at which the Event was generated |
EVENT_SOURCE | VARCHAR(255) | Server name which generated the Event |
EVENT_SCOPE | VARCHAR(255) | Scope of the Event |
EVENT_MODULE | VARCHAR(255) | Module to which the Event belongs |
DESCRIPTION | VARCHAR(255) | Short description of the Event |
EVENT_STATUS | VARCHAR(255) | Event constant representing the type of event |
EXPIRY_TIME | TIMESTAMP | Event expiry time |
USER_NAME | VARCHAR(255) | Name of the user for which the Event was generated |
Table name: USER_EVENTS
| Column Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
EVENT_ID | INTEGER | Auto Generated |
EVENT_CATEGORY | VARCHAR(255) | Category of event, that is, Information, Warning or Error |
GENERATION_DATE | TIMESTAMP | Time at which the Event was generated |
EVENT_SOURCE | VARCHAR(255) | Server name which generated the Event |
EVENT_SCOPE | VARCHAR(255) | Scope of the Event |
EVENT_MODULE | VARCHAR(255) | Module to which the Event belongs |
DESCRIPTION | VARCHAR(255) | Short description of the Event |
EVENT_STATUS | VARCHAR(255) | Event constant representing the type of Event |
EXPIRY_TIME | TIMESTAMP | Event expiry time |
SERVICE_GUID | VARCHAR(255) | The service instance GUID |
TPS_NAME | VARCHAR(255) | The Peer Server name |
TEXT_DATA | VARCHAR(255) | Event Text |
BYTES_DATA | IMAGE | BLOB field representing user event data |
