SMPPSend
SMPPSend microservice is used to send SMS to cell phones using SMPP (Short messsage Peer to Peer) protocol. The communication will be in between Short Message Service Centre (SMSC) which is a message center and SMS application system.
Abbreviations
SMEs: Short message entities
ESMEs: External Short Message Entities. Non-mobile entities that submit messages to, or receive messages from an SMSC
Configuration and Testing
The SMPPSend component connection related properties can be configured in the Configuration Property Sheet (CPS).
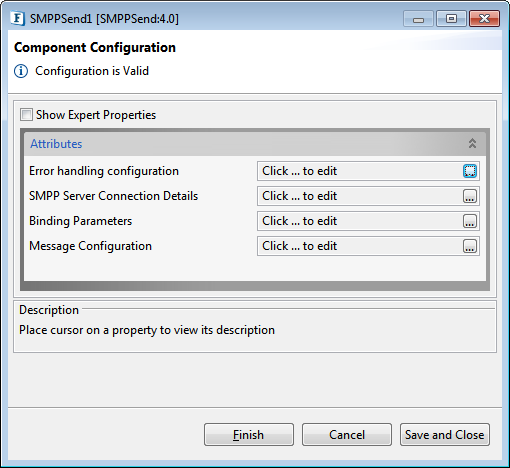
Figure 1: SMPPSend CPS Component Configuration panel
Attributes
Error Handling Configuration
The remedial actions to be taken when a particular error occurs can be configured using this attribute.
Click the ellipsis button against this property to configure Error Handling properties for different types of Errors. By default, the options Log to error logs, Stop service and Send to error port are enabled.
Refer to the Error Handling section in Common Configurations for detailed information.
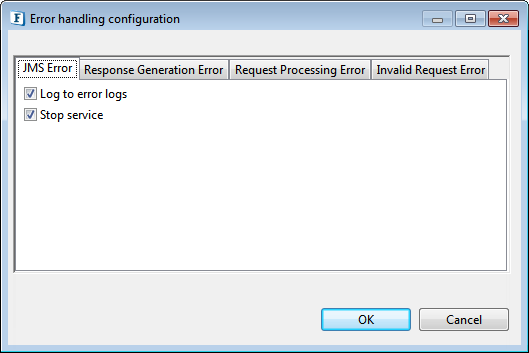
Figure 2: Error Handling Configuration panel
SMPP Server Connection Details
Connection configuration for the SMPP server.
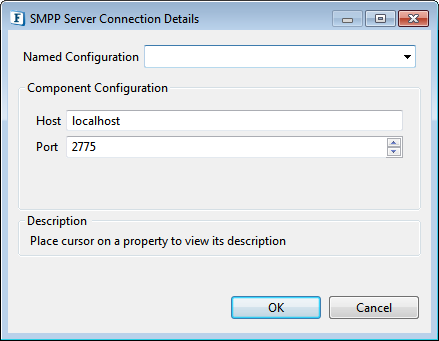
Figure 3: SMPP Server Connection properties
Host: Host name of the SMPP server
Port: Port at which component connects to SMPP server
Binding Parameters
Bind Type
SMPP defines three modes of operation for an ESME: Transmitter, Receiver and Transceiver.
- Bind TX: If bind type is transmitter, connection is allowed to transmit messages only over the connection, it cannot receive any messages.
- Bind RX: If bind type is receiver, connection is allowed to transmit messages only over the connection.
- Bind TRX: If bind type is transreciever, then message submitting and receiving both are allowed.
System ID
It is used to identify an ESME or an SMSC at bind time
Password
The password parameter is used by the ESME to authenticate the identity of the binding SMSC
System Type
The system_type parameter is used to categorize the type of ESME that is binding to the SMSC
Type of Number
Indicates Type of Number of the ESME address
Numbering Plan Indicator
Numbering Plan Indicator for ESME address
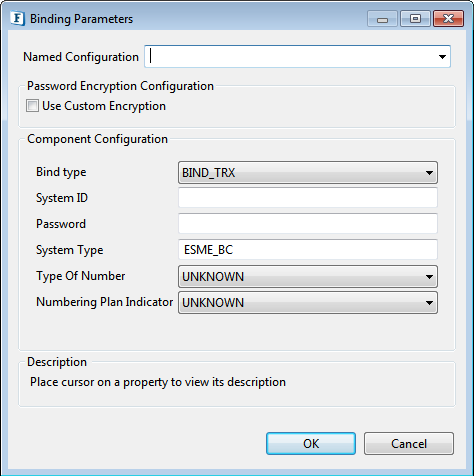
Figure 4: Binding parameters
Message Configuration
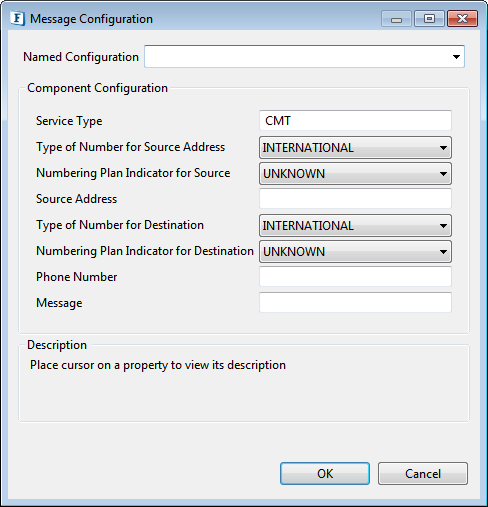
Figure 5: Message Configuration properties
Service Type
The service type parameter can be used to indicate the SMS Application service associated with the message
The following generic Service Types can be defined:
| Service Type | Description |
| NULL | Default |
| CMT | Cellular Messaging |
| CPT | Cellular Paging |
| VMN | Voice Mail Notification |
| VMA | Voice Mail Alerting |
| WAP | Wireless Application Protocol |
| USSD | Unstructured Supplementary Services Data |
Type of Number for Source Address
Type of Number for source address from the below options:
- UNKNOWN
- INTERNATIONAL
- NATIONAL
- NETWROK_SPECIFIC
- SUBSCRIBER_NUMBER
- ALPHANUMERIC
- ABBREVIATED
Numbering Plan Indicator for Source
Numbering Plan Indicator for the source address. Options available are the same as in the above property.
Source Address
Specifies the address of SME which originated this message.
Type of number for Destination
Type of Number for the destination. Options available are the same as in the Type of Number for Source Address property.
Numbering Plan indicator for Destination
Numbering Plan Indicator for the destination. Options available are the same as in the Type of Number for Source Address property.
Phone Number
Destination address of the short message . For mobile terminated messages, this is the directory number of the recipient MS
Message
Short Message that has to be sent.
Expert Properties
Enable the Expert Properties view to configure these properties.
Expert properties are meant for advanced users; use with caution.
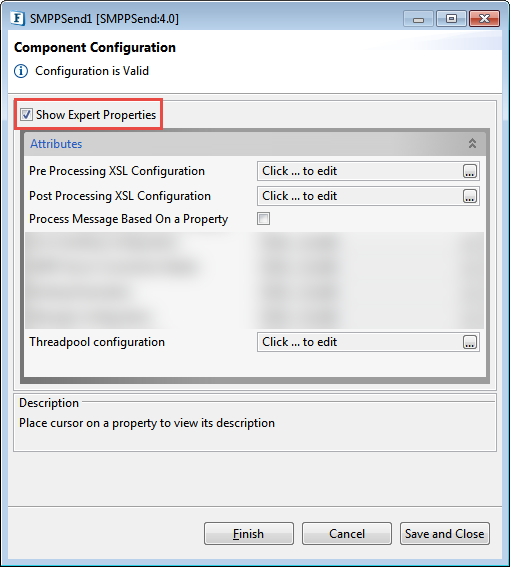
Figure 6: SMPPSend CPS with the Expert Properties enabled and highlighted
Pre Processing XSL Configuration
Pre Processing XSL configuration can be used to transform request message before processing it. Click the ellipses button against the property to configure the properties.
Refer to the Pre/Post Processing XSL Configuration section under the Common Configurations page for details regarding Pre Processing XSL configuration and Post Processing XSL configuration (below).
Post Processing XSL Configuration
Post Processing XSL configuration can be used to transform the response message before sending it to the output port.
Process Message Based on Property
The property helps components to skip certain messages from processing.
Refer to the Process Message Based On a Property section under the Common Configurations page.
Threadpool Configuration
This property is used when there is a need to process messages in parallel within the component, still maintaining the sequence from the external perspective.
Refer to the Threadpool Configuration section under the Common Configurations page.
