Targets
The target configuration encapsulates various back-end/third-party services that need to be invoked by the proxy to fulfill requests. Targets can be HTTP or JMS endpoints.
Click the Targets icon on the left side of the API Projects screen to manage targets.
The endpoint URL specified when creating a project is saved as the default target configuration.
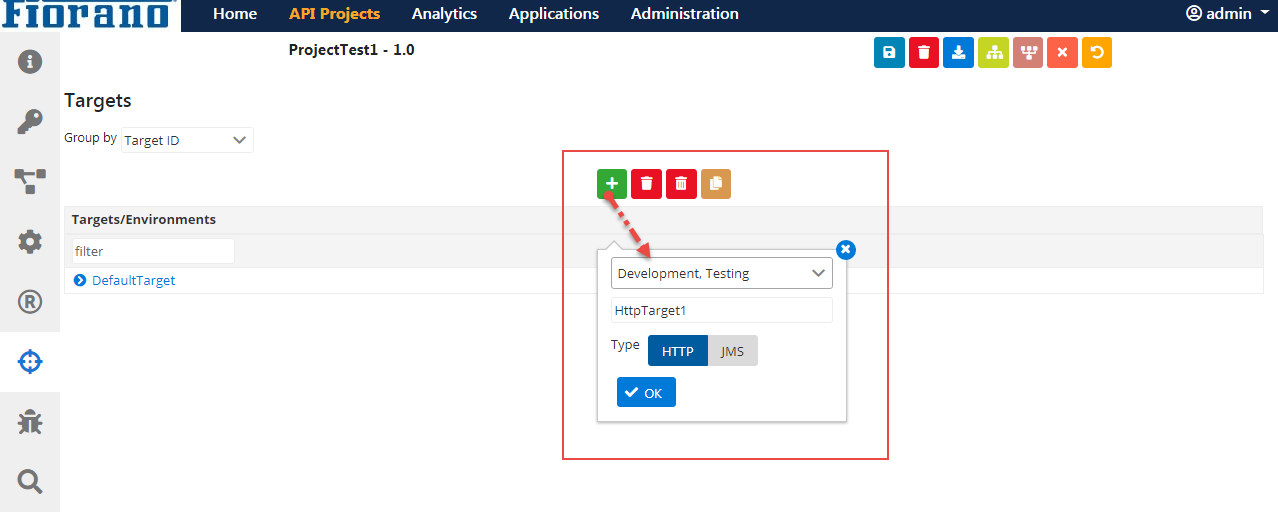
Adding a new target
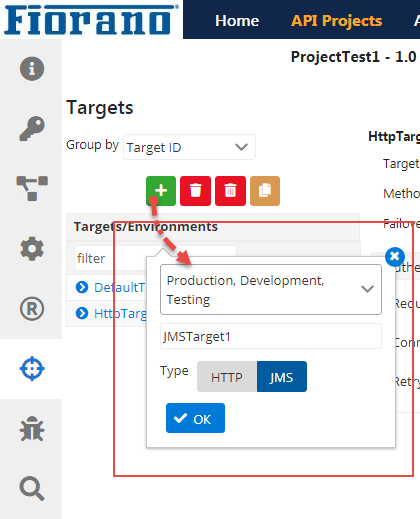
- Click the Add icon.
- Select the Server Group required, provide a Target ID, click the Target Type (HTTP/JMS), and click OK.
- Expand the Target name to select a Server Group to see the HTTP target added. Click the Save icon to save the changes.
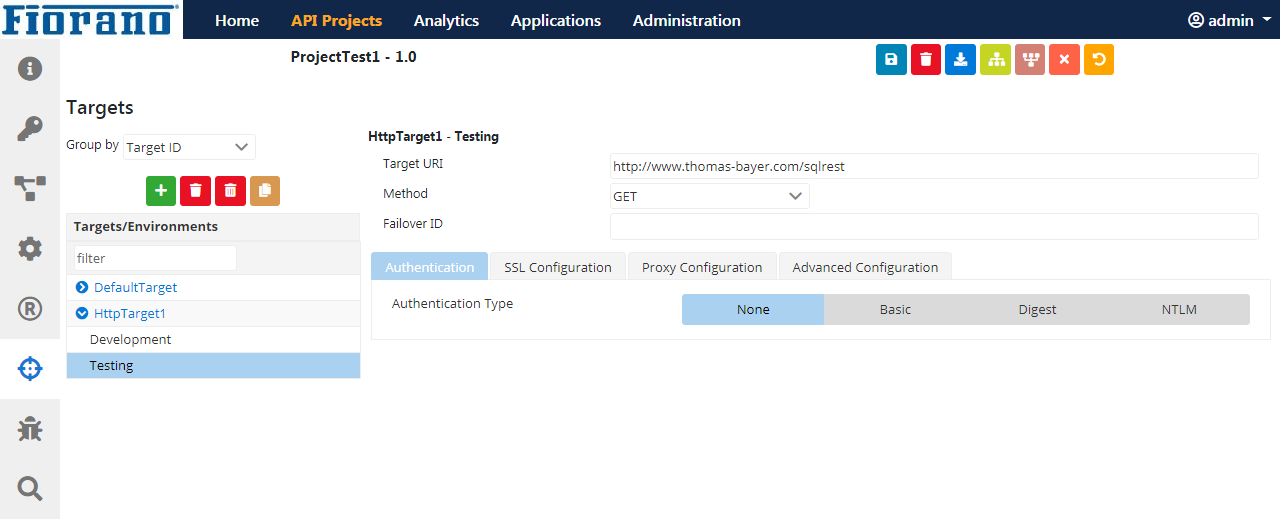
HTTP target
The figure above depicts an HTTP endpoint in Testing environment.
Attribute | Description |
Target URI | URI of the Target endpoint. |
Method | Select a method from the options Get, Post, Put and Delete. |
Failover ID | The ID of the target that needs to be invoked if invocation fails on this server. When a target is not available it is possible to redirect the call to another target using the Failover ID. It is also possible to specify a JMS endpoint as a failover alternative for HTTP endpoint or vice-versa. |
Authentication
This property is used to enable authentication. The three Authentication types are Basic, Digest, and NTLM.
Authentication Type - None
Use the option 'NONE' if authentication is not required (see the figure above).
Authentication Type - Basic
When Authentication Type is 'BASIC', the following attributes need to be specified.
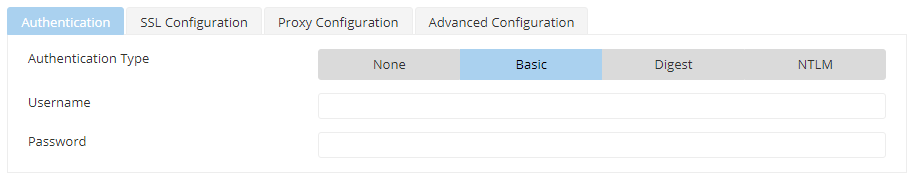
Figure 3: Basic Authentication type attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| User Name | User Name to connect to the web server. |
| Password | Password for the username mentioned. |
Authentication Type - Digest
When Authentication Type is 'DIGEST', the following attributes need to be specified.
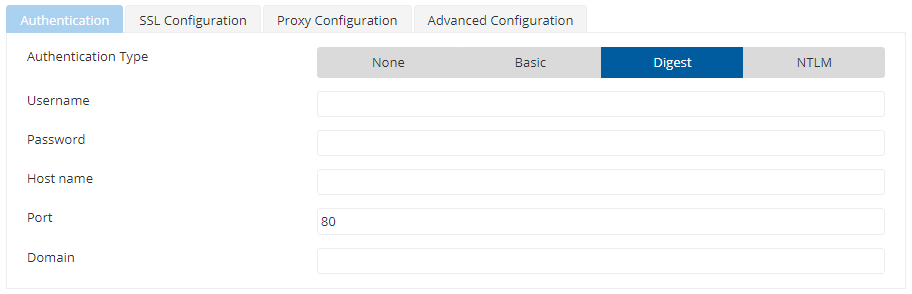
Figure 4: Digest Authentication type attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| User Name | User Name to connect to the web server. |
| Password | Password for the username mentioned. |
| Hostname | Host that is needed to be authenticated with. |
| Port | Port of the host. |
| DOMAIN | Domain name needed by NT Credentials for NT Domain. |
Authentication Type - NTLM
When Authentication Type is 'NTLM', the following attributes need to be specified.
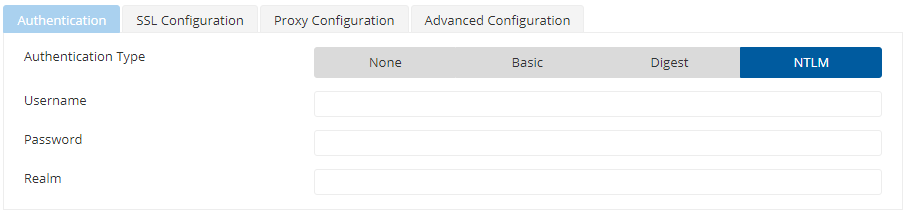
Figure 5: NTLM Authentication type attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| User Name | User Name to connect to the web server. |
| Password | Password for the username mentioned. |
| Password | Realm for authentication scope. |
SSL Configuration
Enable SSL to configure SSL settings to the target. Other properties in this editor get displayed for configuration when this property is enabled.
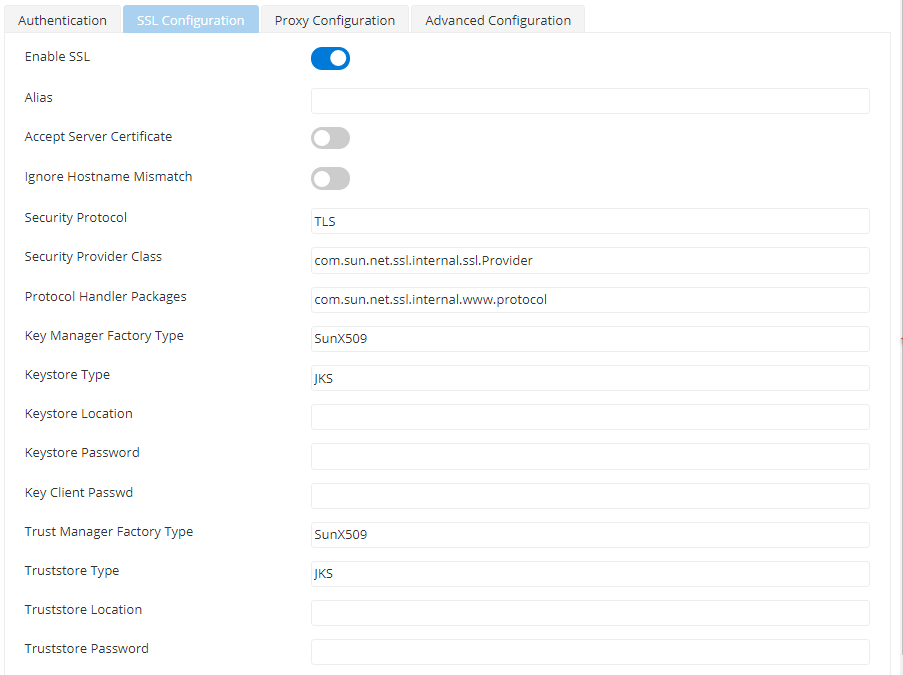
Figure 6: SSL Configuration attributes
Attribute | Description |
Alias | Alias identifies the client to the server. |
Accept Server Certificate | When accessing HTTP URLs, this property determines whether the server certificates should be accepted or not. If selected, the certificate will be accepted without any validation. |
Ignore Hostname Mismatch | If this option is selected, the certificate will be accepted even if the hostname in the certificate does not match with the hostname in the request URL. If it is not selected, an exception is thrown. |
Security Protocol | Determines Security protocol |
Security Provider Class | Determines Security provider class. |
Protocol Handler Packages | Protocol handlers are organized in a package hierarchy similar to content handlers. |
Key Manager Factory Type | Algorithm for the Key Manager Factory. |
Keystore Type | Type of the Key Store whose location is specified by Key Store Location should be specified in the field. |
Keystore Location | Location of the key store file. The KeyStore is used by the component for client authentication. |
Keystore Password | Password of the specified key store can be specified in the field. |
Key Client password | Determines Key Store Client Key |
Trust Manager Factory Type | Algorithm for the Trust Manager Factory. |
Trust Store Location | Location of the trust store file should be specified. TrustStore is a file where digital certificates of trusted sites are stored and retrieved for authentication during an SSL connection. TrustStore is used to authenticate a server in SSL authentication. |
Trust Store Type | Type of Trust Store whose location is specified by property Trust Store Location. |
Trust Store Password | Password of the specified trust store should be specified in the field. |
Proxy Configuration
Enable Proxy to configure proxy settings to the target. Other properties in this editor get displayed for configuration when this property is enabled.
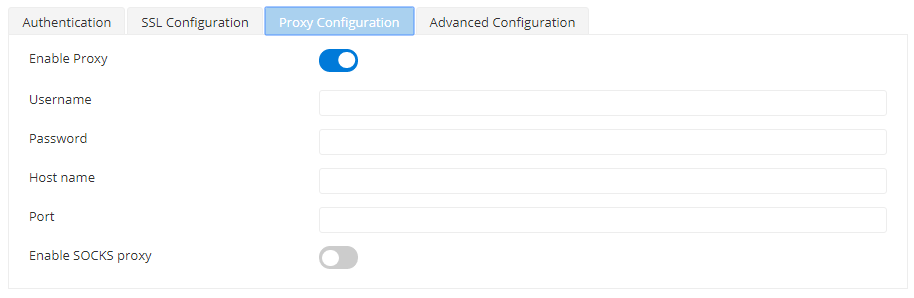
Attribute | Description |
Username | Proxy Username |
Password | Password authenticating the user. |
Host name | Host that is needed to be authenticated. |
Port | Port number of the host. |
Enable SOCKS proxy | Enable if a Socks proxy needs to be enabled. |
Advanced Configuration
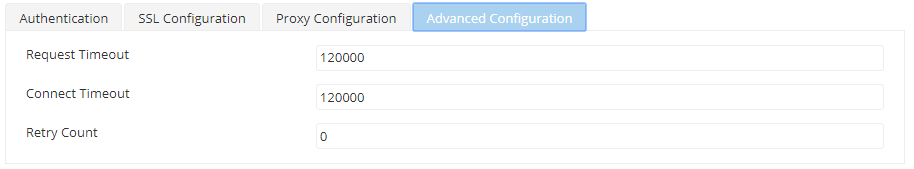
Attribute | Description |
Request Timeout | The maximum time until which it waits for a request. |
Connection Timeout | The maximum time until which it waits for a connection. |
Retry Count | The number of times it needs to retry. |
JMS target
The JMS target can be used to invoke any Message Oriented Middleware systems instead of an HTTP endpoint. It allows the proxy to make a Requestor style call to a JMS Destination and wait for the response from another JMS Destination.
To add a JMS Target, add a new target following the steps in Adding a new target section choosing the Type as JMS.
Expand the JMS target name and click an environment name to set the JMS configuration properties.
The ID of the target that needs to be invoked if invocation fails on this server.
Failover ID (the first property seen in the Target configuration panel) is to redirect the call to another target when a target is not available. It is also possible to specify an HTTP endpoint as a failover alternative for the JMS endpoint and vice-versa.
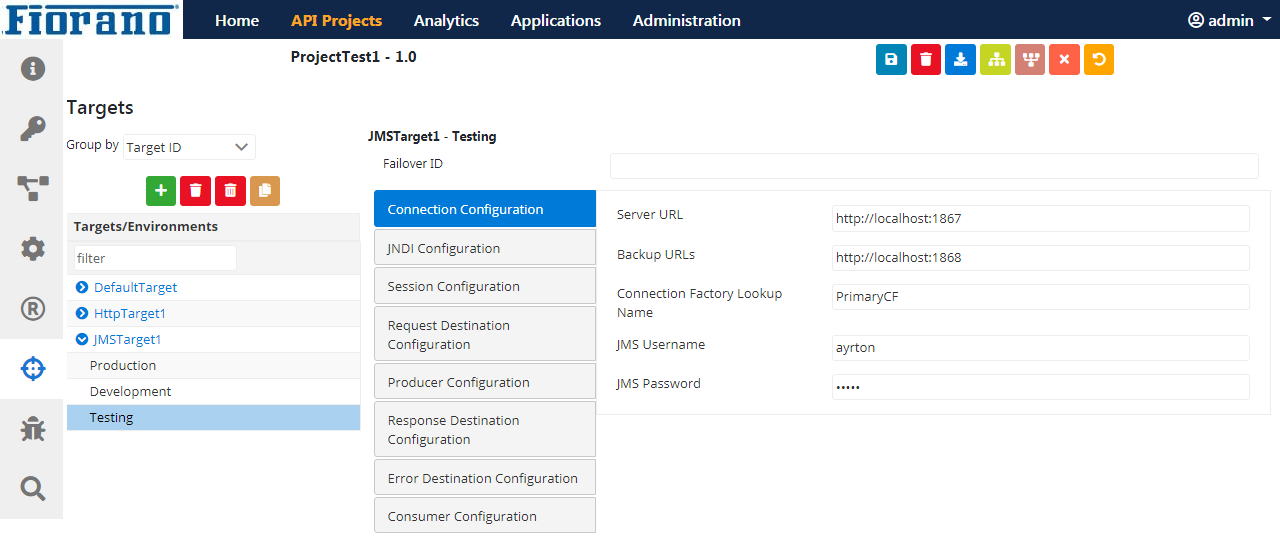
Figure 7: JMS Target Configuration attributes
Connection Configuration
This configuration (see the figure above) helps to connect with a provider and administer JMS.
| Attribute | Description |
Server URL | IP address of the JMS server. |
Backup URLs | The backup URLs to which the component tries to connect if the server specified by the property "server URL" is down. Multiple backup URLs can be specified by separating them with a ';'. |
Connection Factory Lookup Name | Connection Factory Lookup Name. |
JMS Username | The username with which the connection to the server is established. |
JMS Password | Password for the username mentioned. |
JNDI Configuration
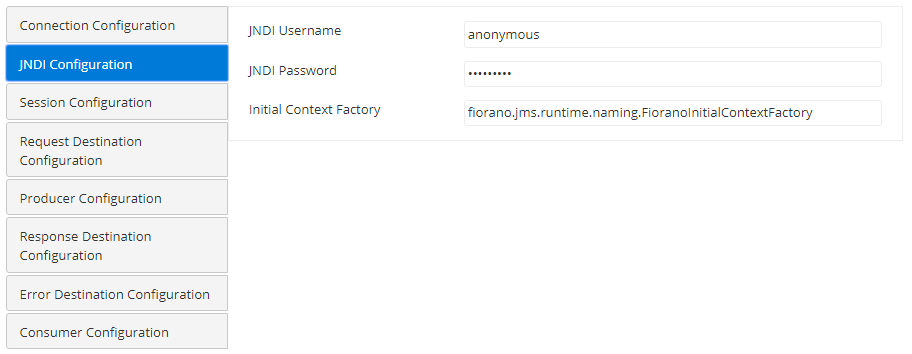
| Attribute | Description |
| JNDI Username | The name with which the user connects to the JNDI server to perform lookup operations. |
| JNDI Password | The password for the JNDI username. |
Initial Context Factory | The name of the initial context factory. The initial context is typically used as a starting point. |
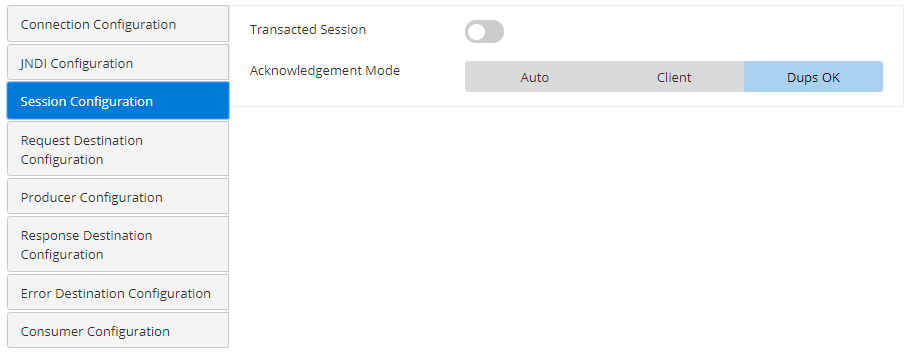
Session Configuration
A session is created from a connection. It is a single-thread context that generates messages to serve multiple consumers.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Is Transacted | A session can be either transacted or non-transacted. Enable this if the session is transacted. When enabled, the acknowledge mode property disappears. |
Acknowledgement Mode | The type of Acknowledgement can be specified here. A session retains messages it consumes until they have been acknowledged. AutoThe session automatically acknowledges a client's receipt of a message either when the session has successfully returned from the receive call or when the message listener, which has been called by the session to process the message, successfully returns. ClientWith this acknowledgment mode, the client acknowledges a consumed message. Dups OKThis acknowledgment mode instructs the session to lazily acknowledge the delivery of messages. |
Request Destination Configuration
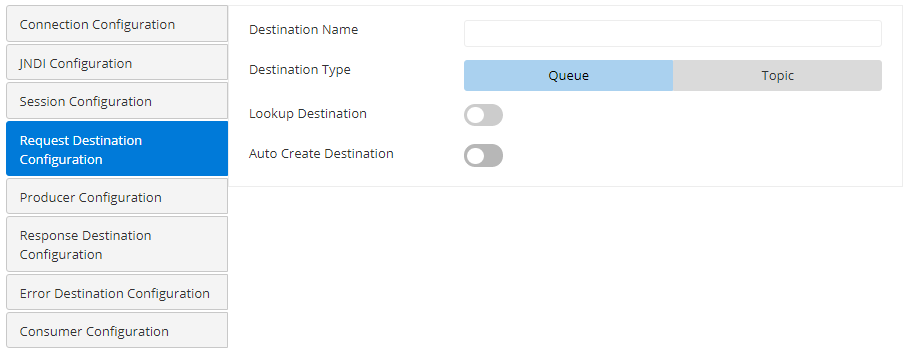
Attribute | Description |
| Destination Name | JNDI name of the topic/queue to be subscribed. |
Destination Type | Specifies whether the destination for the port is a 'Queue' or a 'Topic':
|
| Lookup Destination | Enable this property if the destination is already present and needs to be looked up using JNDI. |
| Auto Create Destination | Enable this property to create a destination if it is not set. |
Producer Configuration
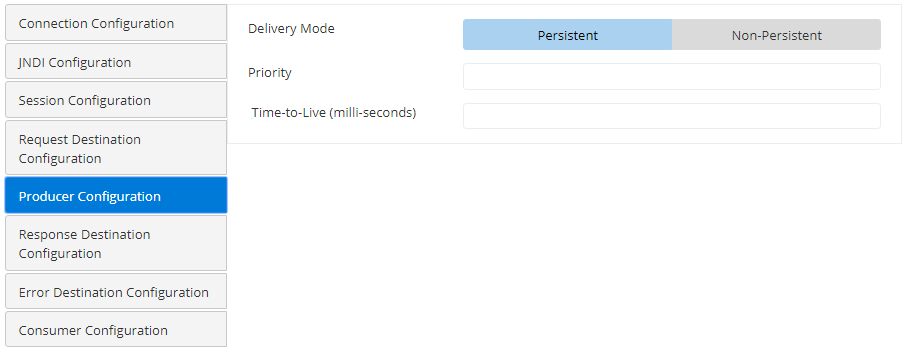
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Delivery Mode | Delivery mode defines whether the message is persistent or non-persistent. PersistentInstructs the JMS provider to take extra care to ensure a message is not lost in transit in case of a JMS provider failure. A message sent with this delivery mode is logged to stable storage when it is sent. Non-persistentNon-persistent delivery mode does not require the JMS provider to store the message or otherwise guarantee that it is not lost if the provider fails. This factor has an impact on the performance. Choose non-persistent messages where appropriate. |
| Priority | The priority of the message to be sent to the destination. |
| Time-to-Live (milliseconds) | The time to live (in milliseconds) of the message to be sent to the destination. After the specified timeout, the message will be discarded. |
Response Destination Configuration
Destination on which response is expected.
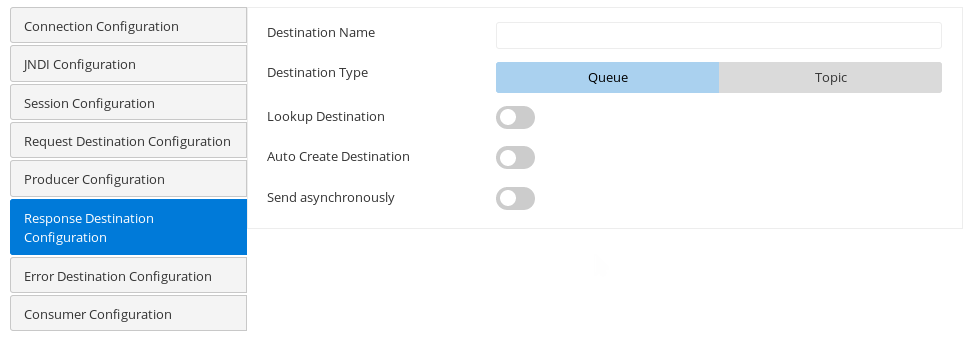
Refer to the Request Destination Configuration section above for the descriptions.
If the Send asynchronously property is enabled, it does not wait for the response after publishing the request to the JMS destination.
Error Destination
Destination on which error is expected.
Refer to the Request Destination Configuration section above for the descriptions.
Consumer Configuration
| Attribute | Description |
| Message Selector | Value for a JMS message property to route the message. |
| Execution Timeout in ms | Maximum time in milliseconds the component should wait for a message. The default value is '0' which specifies infinite wait time which signifies waiting until a message is received. |
