Assign Variables
The assign variable policy can be used to parse the message body to make the various parts of the message available as variables which can be used in the proxy pipeline.
The message body could be any of the following:
- request to a proxy
- response from the target server
- response from an external service call out
For example, a service call made to Google Location JSON service can be parsed to obtain the variableslatitude and longitude of a location and can be used in the flow to build a request to the target server/another service call or responded to the client.
This policy is preferred for simple transformations on huge data when used along with the Build Message policy. For complex transformations, policies or combination of those policies listed below are:
Configuration
To add a variable, perform the following actions in the Assign Variable Policy Configuration page:
Click the Add button and provide a name for the variable to configure source information.
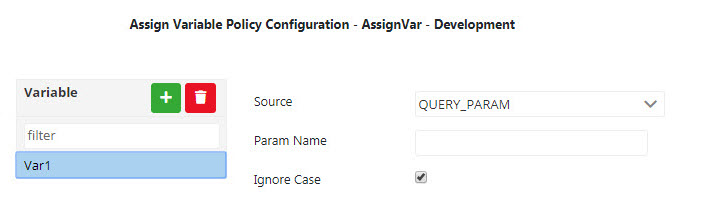
Figure 1: Adding properties- Click the Source drop-down list to select the source from the following options that appear in the list:
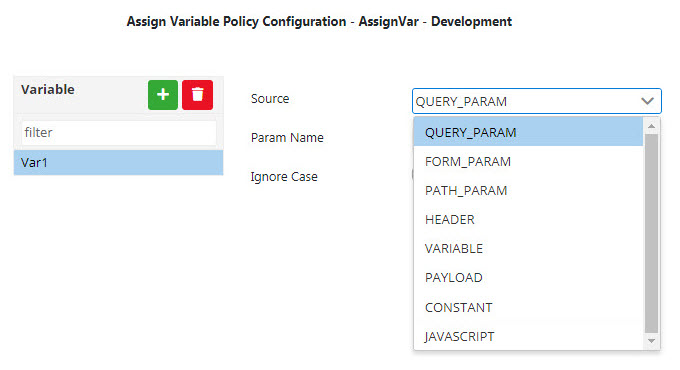
Figure 2: Selecting the Source value- QUERY_PARAM
- FORM_PARAM
- PATH_PARAM
- HEADER
- VARIABLE
- PAYLOAD
- CONSTANT
- JAVASCRIPT
- Provide the substantiating values for the respective source (refer to the sections below) as selected.
Click Save to complete assigning the variable.
Saving variables
Before switching from one variable to another, click the Save button to make sure the configuration is saved properly.
Source
The Source attribute helps to provide extra information which can be used by the Variable parameters that are added. Sources are of different types which may be specified as per requirement. The sections below explain the same.
Query Param
Provide the parameter name in the Param Name field. The value of the query parameter is copied to the variable.
Enable Ignore Case property if the name is not to be Case Sensitive.
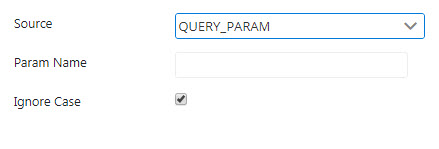
Figure 3: Query Param source properties
Form Param
Provide the parameter name in the Param Name field. The value of the Form Parameter is copied to the variable.
Enable Ignore Case property if the name is not to be Case Sensitive.
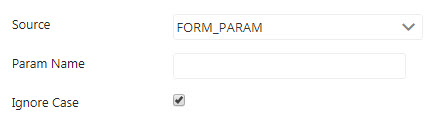
Figure 4: Form Param source properties
Path Param
Provide the path pattern in the Pattern Name property value. This Path will be used by the variable parameter.
Enable Ignore Case property if the name is not to be Case Sensitive.
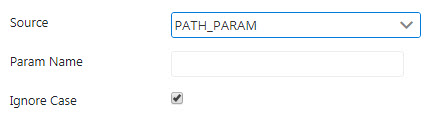
Figure 5: Path Param source properties
Header
Provide the parameter name in the Param Name field. This Header parameter will be used by the variable parameter.
Enable Ignore Case property if the name is not to be Case Sensitive.
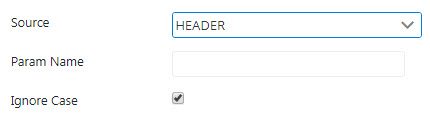
Figure 6: Header source properties
Variable
Provide parameter name in the Param Name field.
Enable Ignore Case property if the name is not to be Case Sensitive.
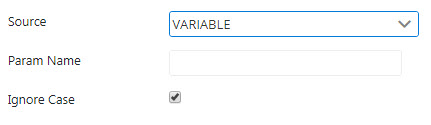
Figure 7: Variable source properties
Payload
Provide a JSON Path value in the JSON Path field to insert the JSON message content to the variable parameter.
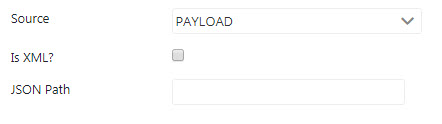
Figure 8: Payload source properties
Choose Is XML option to provide XPath and thereby insert XML in the Variable parameter. To provide Namespaces for the prefixes used in the XPath expression, click the Add button present next to the Namespaces table.
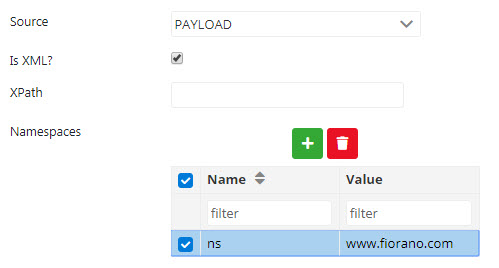
Figure 9: Is XML option under Payload source properties
Constant
Provide a value for the Constant in the Value editor to be used by the Variable parameter.
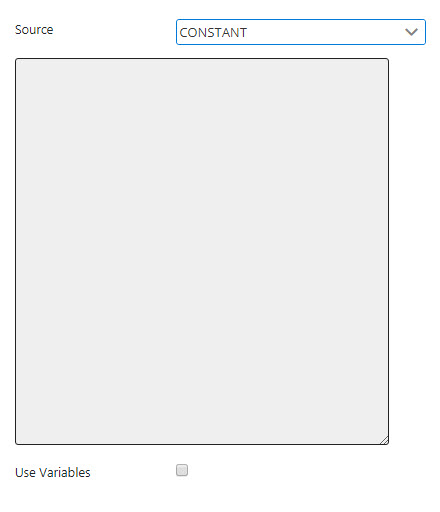
Figure 10: Constant source properties
Choose the Use Variable option to provide a variable prefix and suffix in the Variable Prefix and Variable Suffix fields respectively.
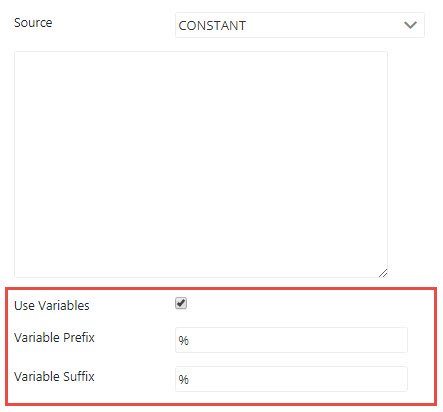
Figure 11: Use Variables option under Constant source properties
Combining variable
The Constant source can be used to concatenate multiple context variables by providing value such as {variable1} constant {variable2}
JavaScript
Provide the script in the Value editor under the Source drop-down list for the Variable parameter to use.
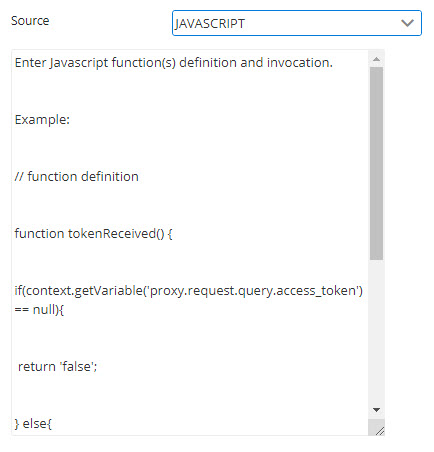
Figure 12: JavaScript source properties
The Javascript option can be used when there is a need to perform complex manipulations instead of simple concatenation which is performed by the constant.
To use this option, the script must contain a function which returns a string. This method must be called inside the javascript block as shown in line no. 8.
function isTokenExists() {
if(context.getVariable("target.request.query.access_token") == null){
return "false";
} else{
return "true";
}
}
isTokenExists();The function can use the variable context which can be used to inject the context of the request. The variable context supports the following methods.
Supported Methods
String getVariable(String name); // returns the context variable value with the name provided as parameter.
String getHeader(String name); // returns value of the header with the name provided as parameter.
String getQueryParam(String name); // returns value of the query parameter with the name provided as parameter.
String getFormParam(String name); // returns value of the form parameter with the name provided as parameter.Examples
Extracting JSON elements
In the example Customizing API Response, different parts of the JSON response from the target server are extracted using this policy.
Using JavaScript
In the example Invoking OAuth and Caching Access Tokens, to calculate and assign the variable to determine whether the token exists in the cache or not, the java script variant is used.
