Creating the .bindings file for Rabbit MQ JMS Provider
Creating the .bindings file
To connect Rabbit MQ using JMS API, 'RefFSContextFactory' has to be used as Initial Context Factory to lookup JNDI objects. In order to lookup, we need to create a '.bindings' file with JNDI administered objects.
To create the bindings file, save a text (.txt) file naming it as ".bindings" and edit the file by providing object definitions represented in Content/Type/Encoding triplet as per requirement.
Name has to be exactly the same as below:
Any change in the name will not serve the purpose.
Objects in the .bindings file
ConnectionFactory
Specify the ConnectionFactory objects in the .bindings file with the corresponding ClassName and FactoryName for each object.
Example
ConnectionFactory/ClassName=javax.jms.ConnectionFactory
ConnectionFactory/FactoryName=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactoryThis .bindings file contains attributes that are used to lookup a ConnectionFactory object and other JNDI resources. Each attribute has a name, a value and the type of variable that holds the value.
Attributes in the ConnectionFactory object
The attributes to lookup connection factory object are name, type, factory, and hostname.
name
A 'name' attribute contains the value 'jms/ConnectionFactory' of type 'String'.
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/0/Content=jms/ConnectionFactory
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/0/Type=name
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/0/Encoding=Stringtype
A 'type' attribute contains the value 'javax.jms.ConnectionFactory' which is of the type 'String'.
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/1/Content=javax.jms.ConnectionFactory
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/1/Type=type
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/1/Encoding=Stringfactory
A 'factory' attribute contains the value 'com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory' which is of the type 'String'.
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/2/Content=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/2/Type=factory
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/2/Encoding=Stringhostname
hostname attribute can be created for ConnectionFactory object as below.
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/3/Content=192.168.1.172
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/3/Type=host
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/3/Encoding=StringDestinations
Similar to that of ConnectionFactory objects, destinations can be specified as objects in .bindings file.
Examples
Considering the destination as queue, to define the destination object, specify the name, type, factory and destinationName attributes.
Queue
Take for example queue name as 'queue1', then the object definition looks like:
# queue1 Queue
queue1/ClassName=javax.jms.Queue
queue1/FactoryName=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory
queue1/RefAddr/0/Content=jms/Queue
queue1/RefAddr/0/Type=name
queue1/RefAddr/0/Encoding=String
queue1/RefAddr/1/Content=javax.jms.Queue
queue1/RefAddr/1/Type=type
queue1/RefAddr/1/Encoding=String
queue1/RefAddr/2/Content=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory
queue1/RefAddr/2/Type=factory
queue1/RefAddr/2/Encoding=String
queue1/RefAddr/3/Content=queue1
queue1/RefAddr/3/Type=destinationName
queue1/RefAddr/3/Encoding=StringTopic
If the destination is Topic, an example of definition of Topic is given below:
# topic1 Topic
topic1/ClassName=javax.jms.Topic
topic1/FactoryName=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory
topic1/RefAddr/0/Content=jms/Topic
topic1/RefAddr/0/Type=name
topic1/RefAddr/0/Encoding=String
topic1/RefAddr/1/Content=javax.jms.Topic
topic1/RefAddr/1/Type=type
topic1/RefAddr/1/Encoding=String
topic1/RefAddr/2/Content=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory
topic1/RefAddr/2/Type=factory
topic1/RefAddr/2/Encoding=String
topic1/RefAddr/3/Content=topic1
topic1/RefAddr/3/Type=destinationName
topic1/RefAddr/3/Encoding=StringdestinationName attribute needs to be specified for the destination object.
Sending AMQP message to the destination
If AMQP message needs to be sent to the destination, then provide additional attributes such as:
- amqp
- amqpExchangeName
- amqpRoutingKey
- amqpQueueName.
queue1/RefAddr/4/Content=true
queue1/RefAddr/4/Type=amqp
queue1/RefAddr/4/Encoding=String
queue1/RefAddr/5/Content=jms.durable.queues
queue1/RefAddr/5/Type=amqpExchangeName
queue1/RefAddr/5/Encoding=String
queue1/RefAddr/6/Content=queue1
queue1/RefAddr/6/Type=amqpRoutingKey
queue1/RefAddr/6/Encoding=String
queue1/RefAddr/7/Content=queue1
queue1/RefAddr/7/Type=amqpQueueName
queue1/RefAddr/7/Encoding=StringIf the message is amqp message, then the configuration of JMSIn:5.0 and JMSOut:5.0 microservices are shown below,
JMSIn:5.0 Configuration
- In the Send Configuration panel, click the ellipsis button for the Message Type Configuration property.
Enable the Use XML Interface property and provide a Message type from the drop-down menu.
By default, it is set to 'Text Message'. If it is an AMQP Message, then 'Map Message' and 'Stream Message' cannot be sent from JMS.
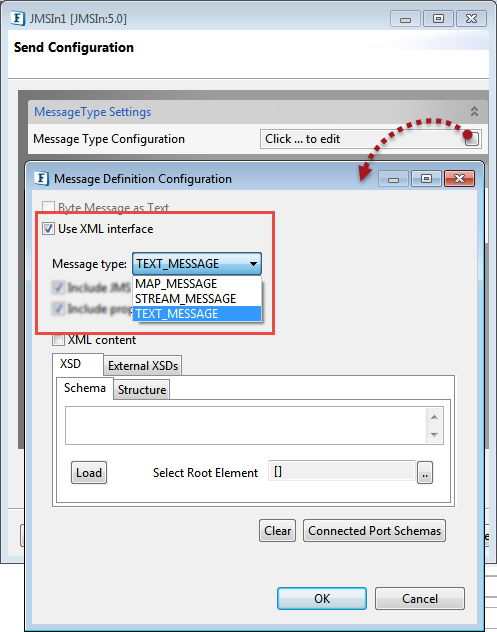
Figure 1: Message Type Configuration property options for JMSIn:5.0
JMSOut5.0 Configration
- In the Receive Configuration page, click the ellipsis button for the Message Type Configuration property.
- If the input does not contain any XML content, then enable the Byte Message as Text property. Else, enable the Use XML Interface property and choose 'BYTE_MESSAGE_AS_TEXT' in the Message Type drop down.


Figure 2: Message Type Configuration property options for JMSOut:5.0
If the message is not an AMQP message, then configure the same Message Type in both JMSIn and JMSOut components.
Sample .bindings file
#Connection Factory Object
ConnectionFactory/ClassName=javax.jms.ConnectionFactory
ConnectionFactory/FactoryName=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/0/Content=jms/ConnectionFactory
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/0/Type=name
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/0/Encoding=String
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/1/Content=javax.jms.ConnectionFactory
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/1/Type=type
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/1/Encoding=String
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/2/Content=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/2/Type=factory
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/2/Encoding=String
# Change this line accordingly if the broker is not at localhost
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/3/Content=192.168.1.172
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/3/Type=host
ConnectionFactory/RefAddr/3/Encoding=String
# test Queue for non-AMQP destination
test/ClassName=javax.jms.Queue
test/FactoryName=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory
test/RefAddr/0/Content=jms/Queue
test/RefAddr/0/Type=name
test/RefAddr/0/Encoding=String
test/RefAddr/1/Content=javax.jms.Queue
test/RefAddr/1/Type=type
test/RefAddr/1/Encoding=String
test/RefAddr/2/Content=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory
test/RefAddr/2/Type=factory
test/RefAddr/2/Encoding=String
test/RefAddr/3/Content=test
test/RefAddr/3/Type=destinationName
test/RefAddr/3/Encoding=String# sample Queue for AMQP destination
sample/ClassName=javax.jms.Queue
sample/FactoryName=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory
sample/RefAddr/0/Content=jms/Queue
sample/RefAddr/0/Type=name
sample/RefAddr/0/Encoding=String
sample/RefAddr/1/Content=javax.jms.Queue
sample/RefAddr/1/Type=type
sample/RefAddr/1/Encoding=String
sample/RefAddr/2/Content=com.rabbitmq.jms.admin.RMQObjectFactory
sample/RefAddr/2/Type=factory
sample/RefAddr/2/Encoding=String
sample/RefAddr/3/Content=sample
sample/RefAddr/3/Type=destinationName
sample/RefAddr/3/Encoding=String
sample/RefAddr/4/Content=true
sample/RefAddr/4/Type=amqp
sample/RefAddr/4/Encoding=String
sample/RefAddr/5/Content=jms.durable.queues
sample/RefAddr/5/Type=amqpExchangeName
sample/RefAddr/5/Encoding=String
sample/RefAddr/6/Content=sample
sample/RefAddr/6/Type=amqpRoutingKey
sample/RefAddr/6/Encoding=String
sample/RefAddr/7/Content=sample
sample/RefAddr/7/Type=amqpQueueName
sample/RefAddr/7/Encoding=StringAdding Dependencies
To use JMS API of RabbitMQ, add the following jars to the JMSAdapters node under System Lib in the Micro Service Repository panel:
amqp-client-4.1.1.jar
fscontext-4.5-b25.jar
rabbitmq-jms-client.jar
To know how to add the jars, refer to the Adding Resources To a Microservice section.
Configuring the Microservice
The JMS microservice connection related properties are configured in the landing panel of the microservice CPS (Managed Connection Factory panel for version 4 and JMS Connection Configuration for version 5).
- In the Provider URL Settings property, specify the JMS Provider as '"RABBIT_MQ".
In the JNDI Settings, Initial Context Factory will be pre-loaded with the value "com.sun.jndi.fscontext.RefFSContextFactory".
The “RefFileSystemContextFactory” element in the Initial Context Factory assumes that JNDI .bindings file is placed at a physical location in the FileSystem.
In the Connection Configuration, specify the location of the JNDI .bindings file in Server URL.
Example
Windows
CODEfile:C:/JNDI-Directory/.bindingsUnix
CODEfile:var/mqm/JNDI-Directory/.bindingsTo validate the connection, click the Test Button. A confirmation message 'Connection created successfully' gets displayed if the connection is succesful.
In the Destination Configuration, when the property 'AutoCreate Destination' is enabled and if the destination provided is not present in the .bindings file, then it will be created dynamically. If 'AutoCreate Destination' is disabled, then the destination must be declared in the .bindings file.
